IO(下)
2019-05-08 07:36:45来源:博客园 阅读 ()

7. 标准输入、输出流
7.1 标准输入流
源数据源是标准输入设备(键盘、鼠标、触摸屏)等输入设备。在java中用http://System.in 得到一个 InputStream 字节输入流。
需求:在控制台输入一句话,然后原样输出
标准输入流以字节流流入内存,如果在控制台中输入字符,字符以默认编码(win简体:gbk)编码成字节进入标准输入流。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 InputStream in = System.in; 3 4 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 5 int len; 6 // buf中包含回车和换行 7 len = in.read(buf); 8 9 String str = new String(buf, 0, len); 10 // System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buf)); 11 System.out.println(str); 12 }
需求:从控制台高效读取一行数据。把一首诗写入文件。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 InputStream in = System.in; 3 InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(in, "GBK"); 4 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); 5 6 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\k.txt"); 7 FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file); 8 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer); 9 10 String end = "bye"; 11 while(true) { 12 String line = br.readLine(); 13 if(line.equals(end)) { 14 break; 15 } 16 17 bw.write(line); 18 // bw.newLine(); 19 } 20 21 bw.flush(); 22 23 bw.close(); 24 writer.close(); 25 26 }
7.2 标准输出流
数据目的地是标准输出设备(显示器)等输出设备。在java中用System.out得到一个 PrintStream 字节输出流(字节打印流)。提供了更强大的
- print()
- println()
打印方法用于打印各种数据类型。
需求:读取文件,显示到标准输出设备
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\k.txt"); 4 5 FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); 6 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); 7 8 PrintStream ps = System.out; 9 10 String line; 11 while( (line=br.readLine())!=null ) { 12 ps.println(line); 13 } 14 }
PrintStream 打印的所有字符都使用平台的默认字符编码将字节转换为字符。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 String str = "hello中国"; 4 byte[] buf = str.getBytes("utf-8"); 5 6 PrintStream ps = System.out; 7 ps.write(buf); 8 9 }
输出 - hello涓浗
8. Scanner
Scanner 除了可以用于获得键盘输入之外,还可以直接读取文件内容。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 // 扫描平台默认编码的文件 4 /*File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\j.txt"); 5 Scanner sc = new Scanner(file); 6 */ 7 8 // 扫描指定编码的文件 9 Scanner sc = new Scanner(new FileInputStream(new File("d:\\javatest\\j-utf8.txt")), "UTF-8"); 10 11 String line; 12 while (sc.hasNextLine()) { 13 line = sc.nextLine(); 14 System.out.println(line); 15 } 16 17 }
9. 序列化
把内存中的对象永久保存到硬盘的过程称为对象序列化,也叫做持久化。
把硬盘持久化的内存恢复的内存的过程称为对象反序列化。
9.1 Serializable
类通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能。未实现此接口的类将无法使其任何状态序列化或反序列化,并抛出异常
Exception in thread "main" java.io.NotSerializableException: cn.sxt05.serializable.Student
at java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeObject0(ObjectOutputStream.java:1184)
at java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(ObjectOutputStream.java:348)
at cn.sxt05.serializable.Test01.main(Test01.java:22)
Serializable接口没有方法或字段,仅用于标识可序列化的语义。
9.2 序列化对象
ObjectOutputStream 继承于OutputStream,专门用于把对象序列化到本地。提供了
- writeXxx() 写入一个基础类型数据(不常用);
- writeObject() 用于写入一个对象。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 Student stu = new Student("001", "小明", 20, Gender.男); 4 5 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\l.txt"); 6 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); 7 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); 8 9 oos.writeObject(stu); 10 11 oos.close(); 12 out.close(); 13 }
9.3 反序列化对象
ObjectInputStream 继承于InputStream ,专门用于把本地持久化内容反序列化到内存,提供了
- readXXX() 读取一个基础类型数据;
- readObject() 用于读取一个序列化内容并返回一个对象。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\l.txt"); 4 5 6 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); 7 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in); 8 9 Student student = (Student) ois.readObject(); 10 System.out.println(student.getId()); 11 System.out.println(student.getName()); 12 System.out.println(student.getAge()); 13 System.out.println(student.getGender()); 14 15 ois.close(); 16 in.close(); 17 }
9.4 序列号版本
当序列化完成后,后期若升级程序中的类(Student),此时再反序列化时会出现异常,异常原因:序列化流的serialVersionUID和升级后类的版本不匹配。
Exception in thread "main" java.io.InvalidClassException: cn.sxt05.serializable.Student; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID = -6288733824962181189, local class serialVersionUID = 1690603786167234505
at java.io.ObjectStreamClass.initNonProxy(ObjectStreamClass.java:687)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readNonProxyDesc(ObjectInputStream.java:1876)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readClassDesc(ObjectInputStream.java:1745)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readOrdinaryObject(ObjectInputStream.java:2033)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject0(ObjectInputStream.java:1567)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject(ObjectInputStream.java:427)
at cn.sxt05.serializable.Test02.main(Test02.java:16)
所以若要对对象进行序列号,建议添加序列化版本号,可以通过 IDE 自动生成唯一 ID。
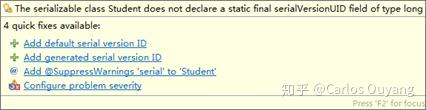
然后程序添加以下内容,问题解决。
1 private static final long serialVersionUID = -1003763572517930507L;
9.5 transient
开发过程中,如果想忽略某些字段不让其序列化时,可以使用transient修饰。
1 public class Student implements Serializable { 2 3 private static final long serialVersionUID = 7222966748321328300L; 4 5 private String id; 6 private transient String name; //将不被序列化 7 private transient int age; //将不被序列化 8 private Gender gender; 9 private String phone; 10 }
10 DataInputStream/DataOutputStream
DataOutputStream 继承OutputStream,专门用于把基本java数据类型写入输出流。提供了writeXXX 写入基本java数据类型。
DataInputStream 继承于InputStream,允许应用程序以与机器无关方式从底层输入流中读取基本 Java 数据类型。
DataInputStream/DataOutputStream 特别适合读取/写入在网络传输过程中的数据流。
写入基本java数据类型
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\n.txt"); 4 FileOutputStream out= new FileOutputStream(file); 5 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out); 6 7 dos.writeInt(10); 8 dos.writeUTF("hello中国"); 9 10 dos.close(); 11 out.close(); 12 13 System.out.println("写入完成"); 14 15 }
读取基本java数据类型
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\n.txt"); 4 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); 5 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in); 6 7 int a = dis.readInt(); 8 String str = dis.readUTF(); 9 10 System.out.println(a); 11 System.out.println(str); 12 13 }
注意:
以什么顺序写入基本java数据类型,就以什么顺序读取基本java数据类型。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/carlosouyang/p/10830530.html
如有疑问请与原作者联系
标签:
版权申明:本站文章部分自网络,如有侵权,请联系:west999com@outlook.com
特别注意:本站所有转载文章言论不代表本站观点,本站所提供的摄影照片,插画,设计作品,如需使用,请与原作者联系,版权归原作者所有
- Spring Security OAuth 格式化 token 输出 2020-06-08
- 架构师需要懂的环境配置标准化 2020-05-24
- 4-JVM 参数 2020-05-14
- JAVA面试题:输出100以内所有的素数 2020-05-09
- java 输入string 2020-04-30
IDC资讯: 主机资讯 注册资讯 托管资讯 vps资讯 网站建设
网站运营: 建站经验 策划盈利 搜索优化 网站推广 免费资源
网络编程: Asp.Net编程 Asp编程 Php编程 Xml编程 Access Mssql Mysql 其它
服务器技术: Web服务器 Ftp服务器 Mail服务器 Dns服务器 安全防护
软件技巧: 其它软件 Word Excel Powerpoint Ghost Vista QQ空间 QQ FlashGet 迅雷
网页制作: FrontPages Dreamweaver Javascript css photoshop fireworks Flash
